BOJ 6549 히스토그램에서 가장 큰 직사각형
사용한 알고리즘
- 그리디 알고리즘
알고리즘 설명
- 왼쪽에 있는 직사각형부터 오른쪽 끝까지 점검을 시작한다.
- 스택을 하나 생성하고, 아래를 반복한다.
- Step1. 스택에 top에 있는 값이, 현재 점검하고 있는 직사각형의 높이보다 큰 경우 스택에서 값을 현재 직사각형보다 작을때 까지 뽑는다.
- Step1-1. 이후 뽑아진 구간과 현재까지 만들어지는 사각형 하나를 만든다.
- Step2. 현재 직사각형 위치를 저장하고, 다음으로 직사각형을 판단한다.
- Step3. Step1과 Step2를 모든 직사각형을 확인할때 까지 반복한다.
Step4. Step3 이후 스택에 남아있는 값으로 직사각형을 만들어본다.
- 예시는 아래와 같다.
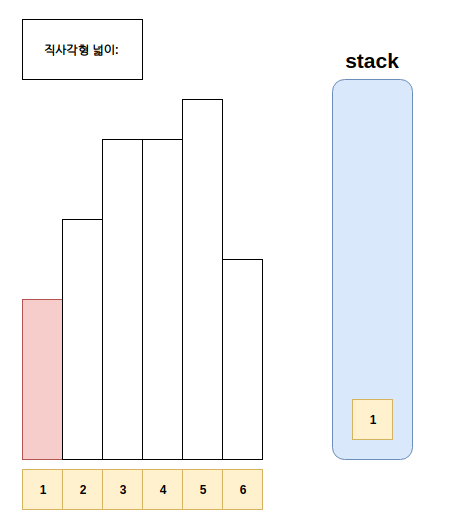
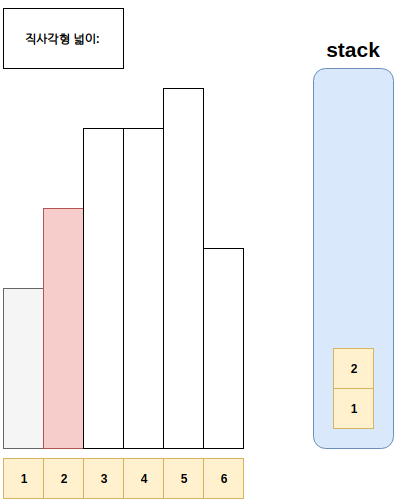

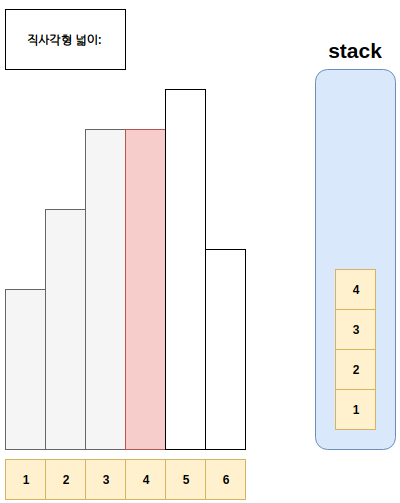
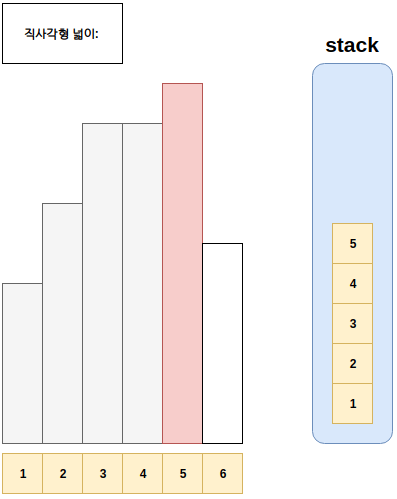
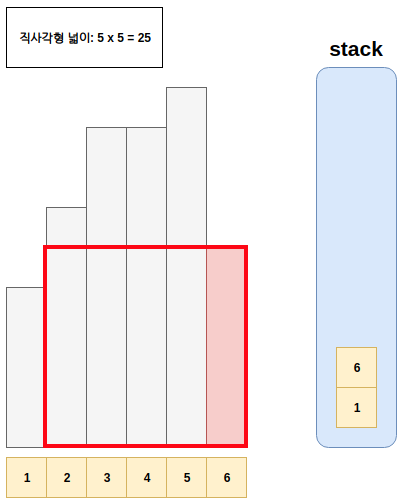
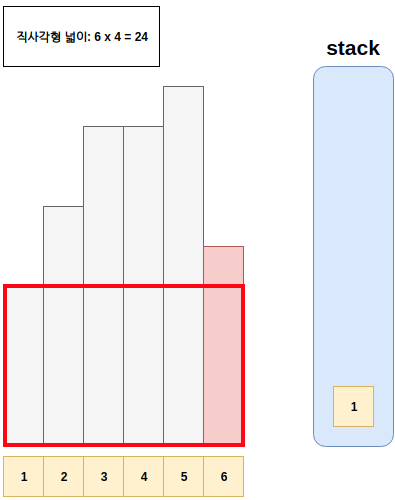
풀이
// baekjoon 6549 yechan
#include <cstdio>
#include <stack>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int MAX_N=100001;
int N;
ll H[MAX_N];
int main() {
while (1) {
scanf("%d", &N);
if (!N) break;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++)
scanf("%lld", &H[i]);
ll ret=0;
stack<int> st;
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
while (!st.empty() && H[st.top()] > H[i]) {
int height = H[st.top()];
st.pop();
int width = i;
if (!st.empty())
width=i-st.top()-1;
ret=max(ret, 1LL*height*width);
}
st.push(i);
}
while (!st.empty()) {
int height = H[st.top()];
st.pop();
int width = N;
if (!st.empty())
width = N-st.top()-1;
ret=max(ret, 1LL*height*width);
}
printf("%lld\n", ret);
}
return 0;
}
